neo_waypoint_following¶
neo_waypoint_follower is a ROS 2 package utilized for waypoint following of any mobile robots.
It provides two core functionalities:
- Waypoint Saving: Save waypoints from RViz
MarkerArraytopics to a YAML file via a ROS 2 service. - Waypoint Looping: Autonomously loop through saved waypoints using the Nav2 navigation stack, with flexible control over repetition, timing, and failure handling, via a ROS 2 service.
Note
This package is not necessarily restricted to neobotix robots or it’s simulation. Provided the Nav2 stack as been configured on your robot, this package could be utilized freely.
Nodes¶
save_waypoints_server¶
Purpose:
Listens to a MarkerArray topic (e.g., from RViz) and saves the received waypoints to a YAML file on request.
Parameters:
waypoints_topic(string): Topic to subscribe for waypoints (default:/waypoints)output_file(string): Path to save the waypoints YAML file
Service:
/save_waypoints(std_srvs/srv/Trigger): Saves the latest received waypoints to the specified YAML file.
waypoint_looper¶
Purpose: Loads waypoints from a YAML file and sends navigation goals to the Nav2 stack, looping through the waypoints as configured.
Parameters:
yaml_file(string): Path to the waypoints YAML fileframe_id(string): Frame ID for waypoints (default:map)repeat_count(int): Number of times to repeat the waypoint loop (default:100)wait_at_waypoint_ms(int): Time to wait at each waypoint in milliseconds (default:500)stop_on_failure(bool): Stop looping on navigation failure (default:true)action_name(string): Nav2 action server name (default:/navigate_to_pose)
Services:
/start_waypoint_loop(std_srvs/srv/Trigger): Starts the waypoint loop/stop_waypoint_loop(std_srvs/srv/Trigger): Stops the waypoint loop
Launch¶
The package provides a launch file for easy configuration and startup:
ros2 launch neo_waypoint_follower waypoint_follower_launch.py
Launch Arguments¶
| Argument | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
waypoints_topic |
/waypoints |
Topic to listen to for waypoints |
waypoints_yaml |
<pkg>/config/waypoints.yaml |
Path to the waypoints YAML file (save & loop) |
frame_id |
map |
Frame ID for waypoints |
repeat_count |
100 |
Number of times to repeat the loop |
wait_at_waypoint_ms |
500 |
Time to wait at each waypoint (ms) |
stop_on_failure |
true |
Stop looping on navigation failure |
Example:
ros2 launch neo_waypoint_follower waypoint_follower_launch.py repeat_count:=10 wait_at_waypoint_ms:=1000
Usage with a simulation package¶
Launch the Simulation and Navigation Stack
Open separate terminals and run the following commands in order:
- Launch the simulation:
ros2 launch rox_bringup bringup_sim_launch.py
- Launch the navigation stack (with simulation time):
ros2 launch rox_navigation navigation.launch.py use_sim_time:=True- Launch RViz:
ros2 launch neo_nav2_bringup rviz_launch.py
- Launch the waypoint follower (with example arguments):
ros2 launch neo_waypoint_follower waypoint_follower_launch.py repeat_count:=10 wait_at_waypoint_ms:=1000
To load a custom waypoints YAML file:
ros2 launch neo_waypoint_follower waypoint_follower_launch.py load_waypoints_path:=/home/adarsh/waypoints_test.yamlMake sure your custom YAML file follows the template provided in
config/waypoints_template.yaml.Add and Use Waypoints
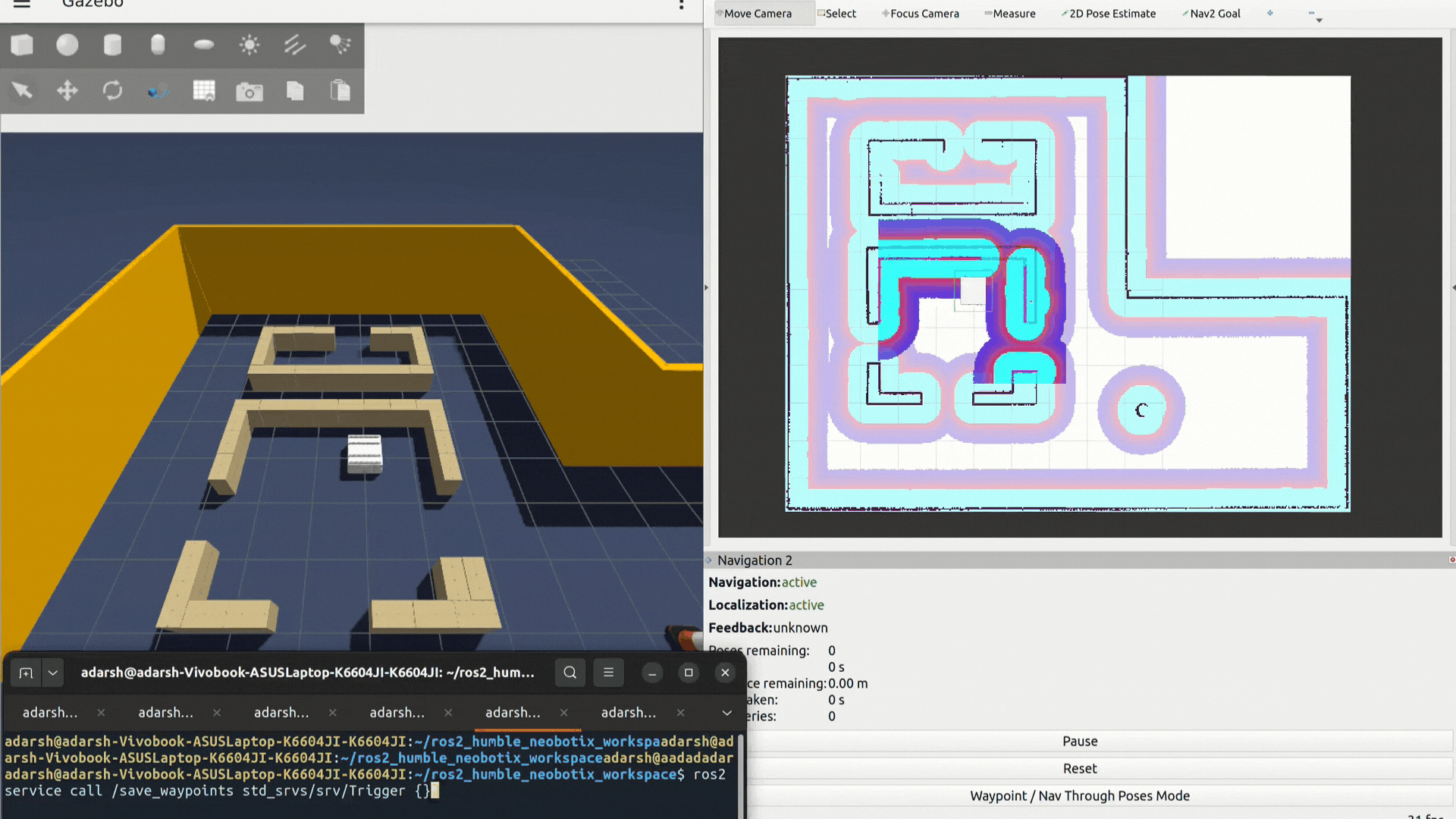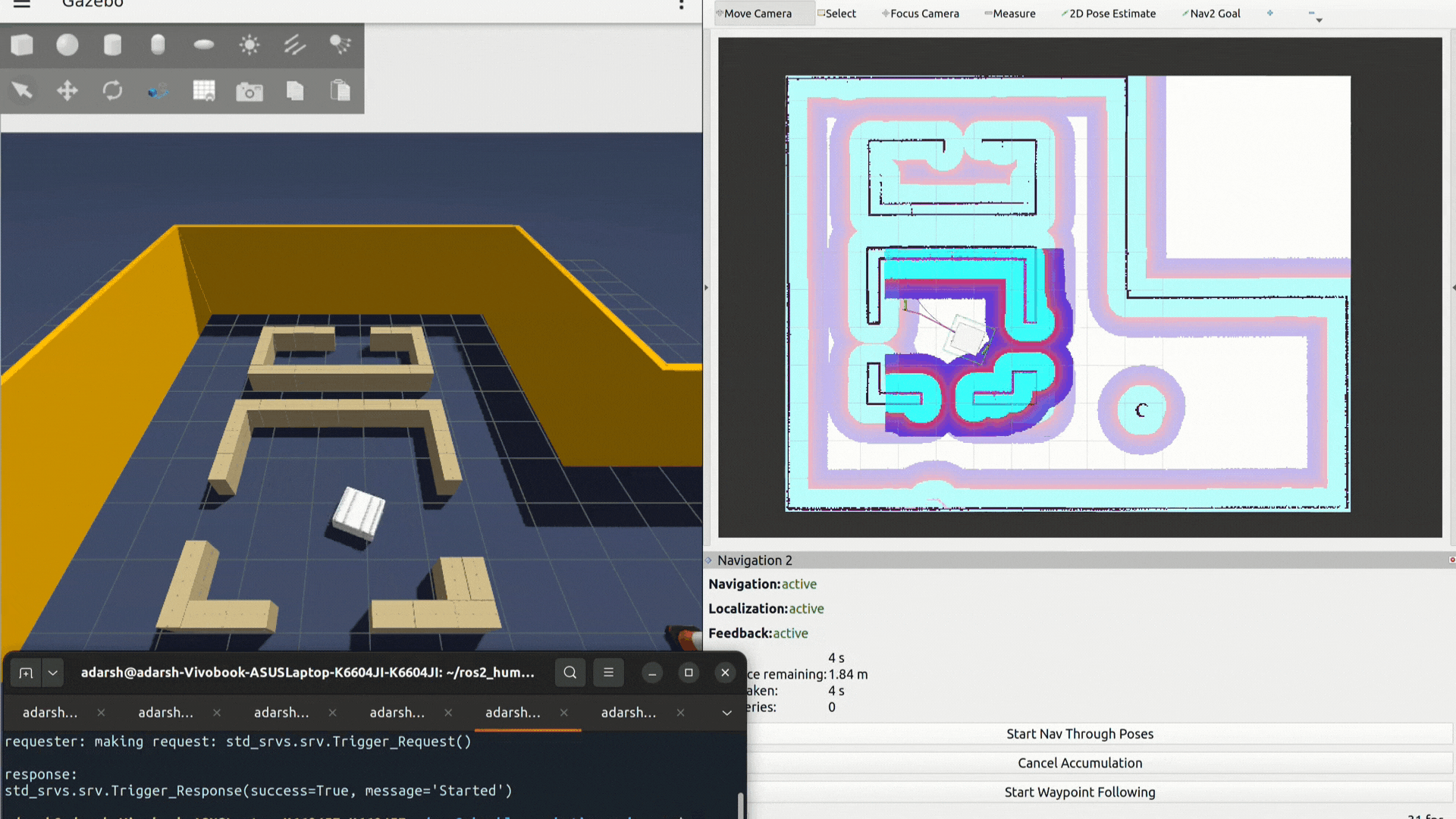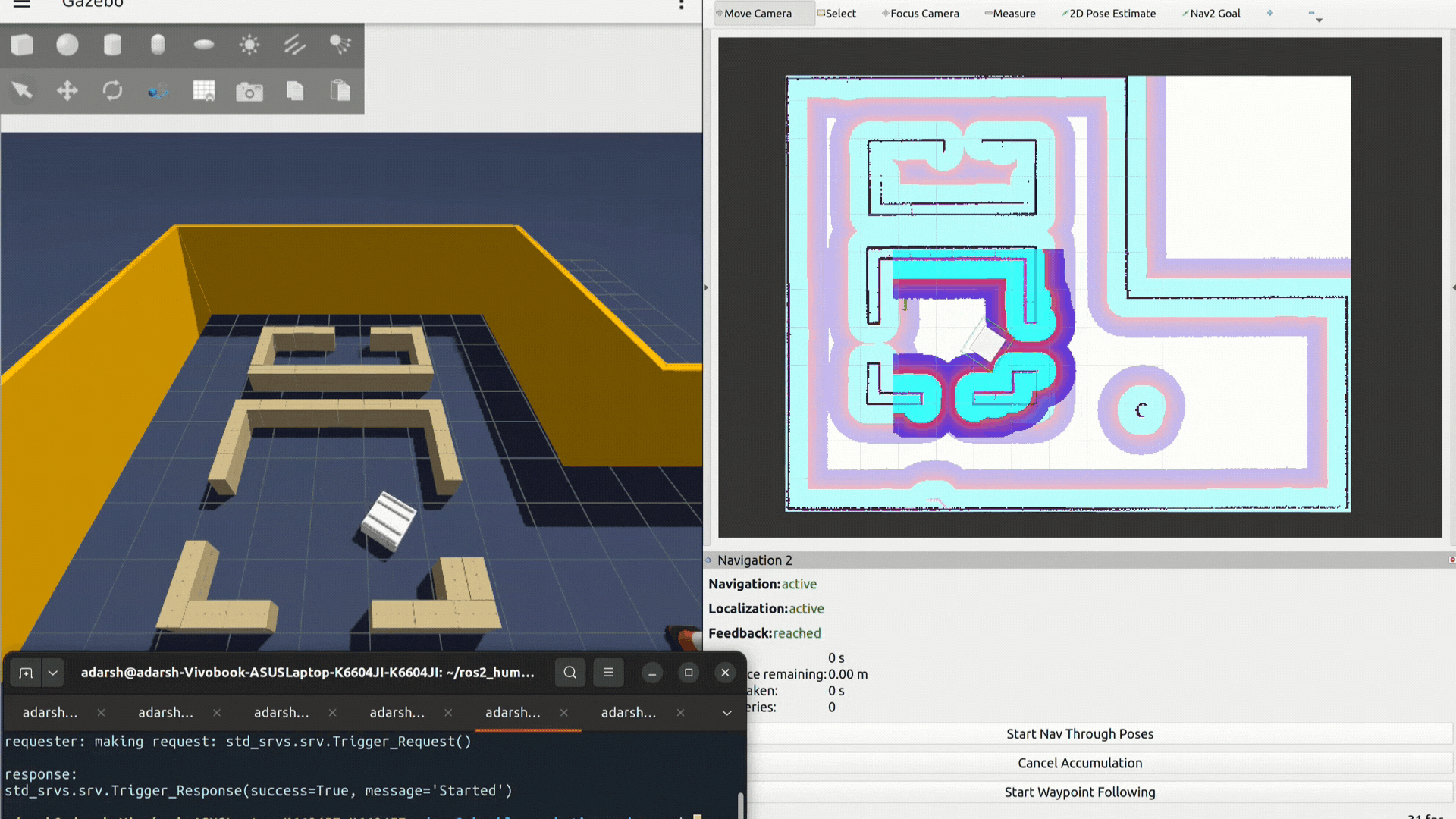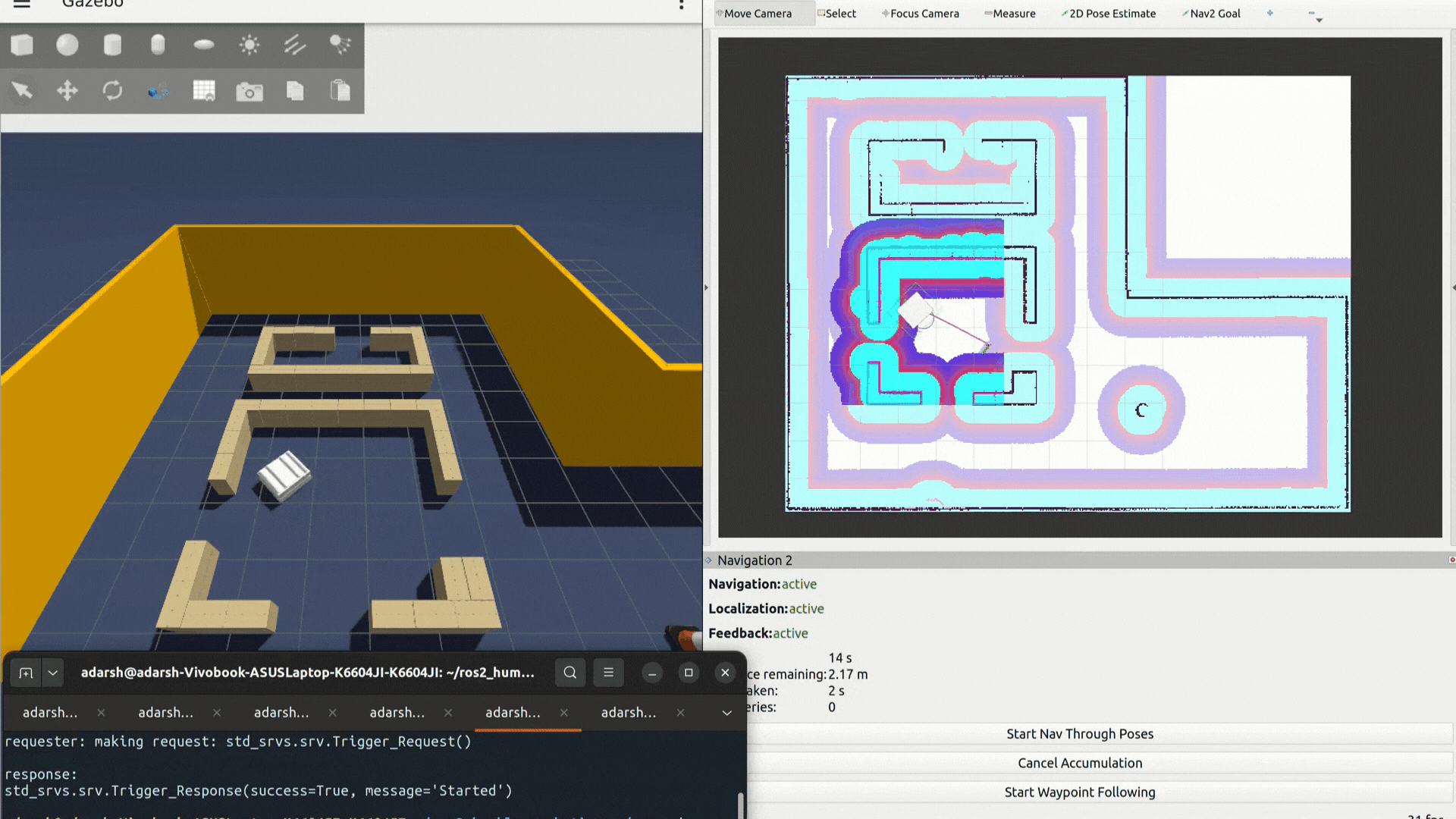
- Add waypoints in RViz using the Navigation2 Panel.
Select the
Waypoint / Nav Thru Poses Mode. When you add waypoints using theNav2 Goalmarkers, they are automatically published to the/waypointstopic by the Nav2 stack. Once all desired waypoints are marked, do not choose any options from the Nav2 panel. - Save waypoints:
ros2 service call /save_waypoints std_srvs/srv/Trigger {}- Start waypoint looping:
ros2 service call /start_waypoint_loop std_srvs/srv/Trigger {}- Stop waypoint looping:
ros2 service call /stop_waypoint_loop std_srvs/srv/Trigger {}- Add waypoints in RViz using the Navigation2 Panel.
Select the